Rubber feet
Engineered Rubber Feet That Ensure Stability and Withstand the Test of Time
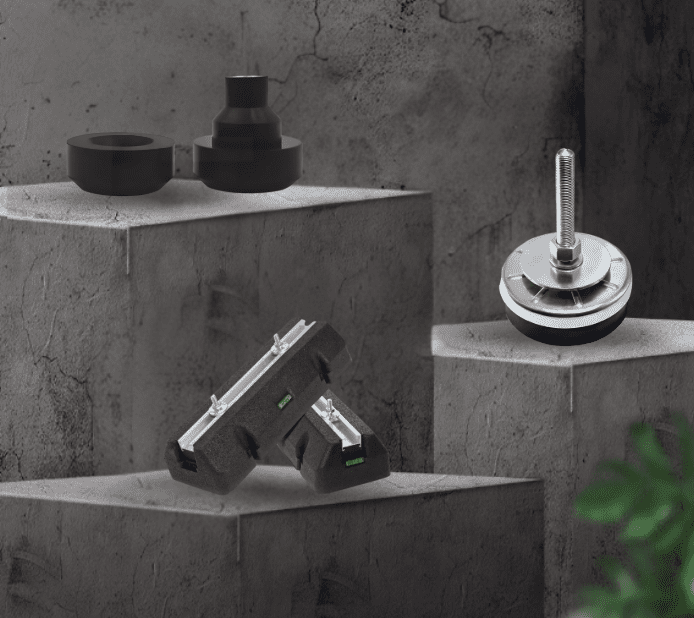

Our products
Rubber feet
Product Showcase
Rubber Feet – Quiet Strength Underneath.
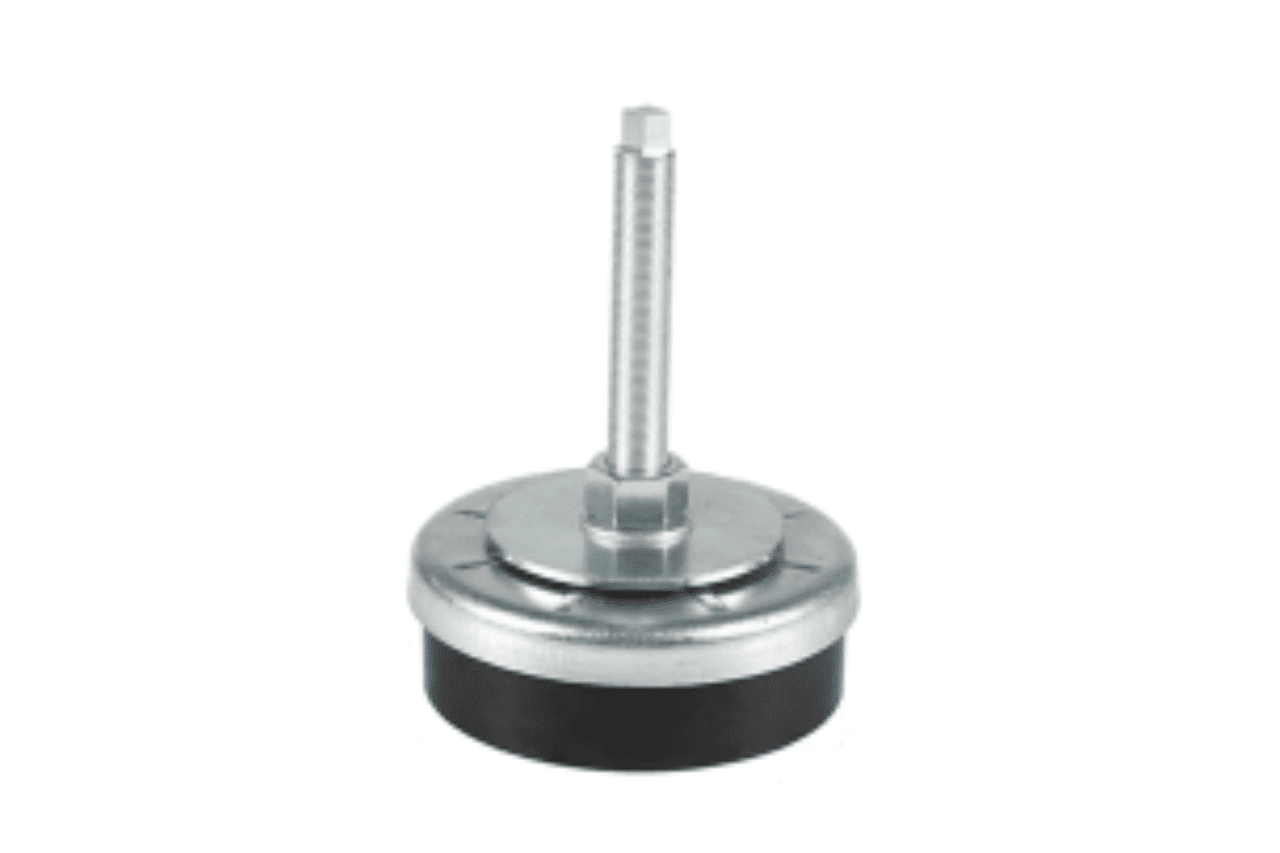
Rubber Feet
Rubber Feet
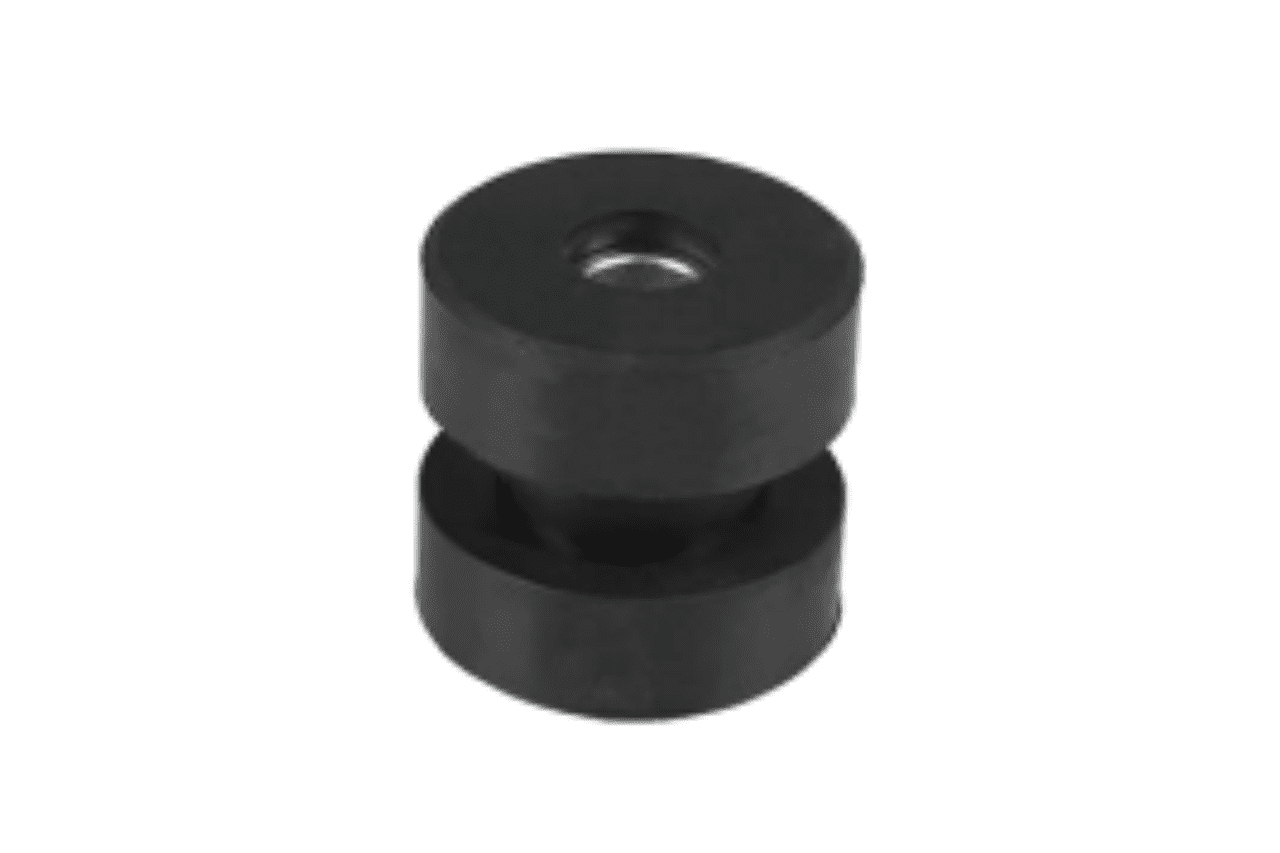
Rubber Pad
Rubber Pad
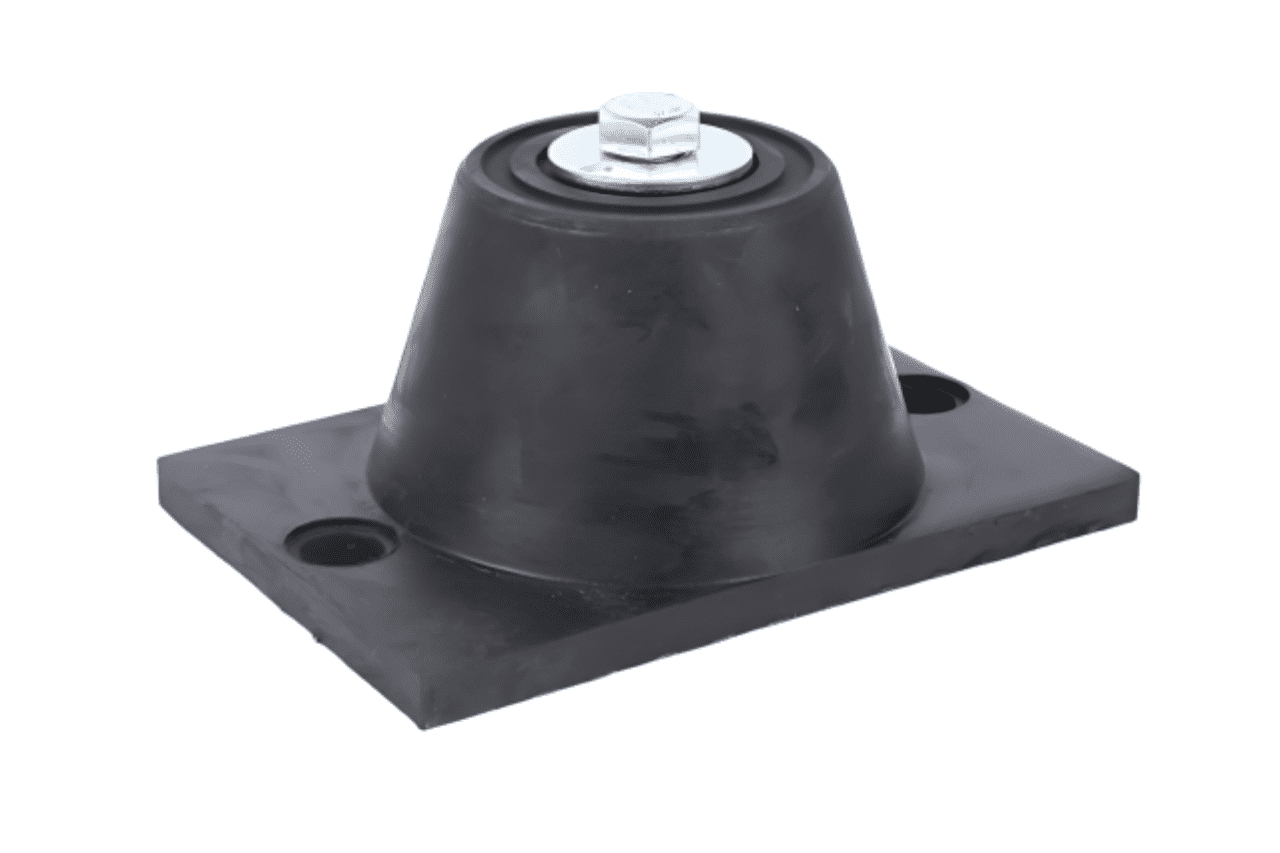

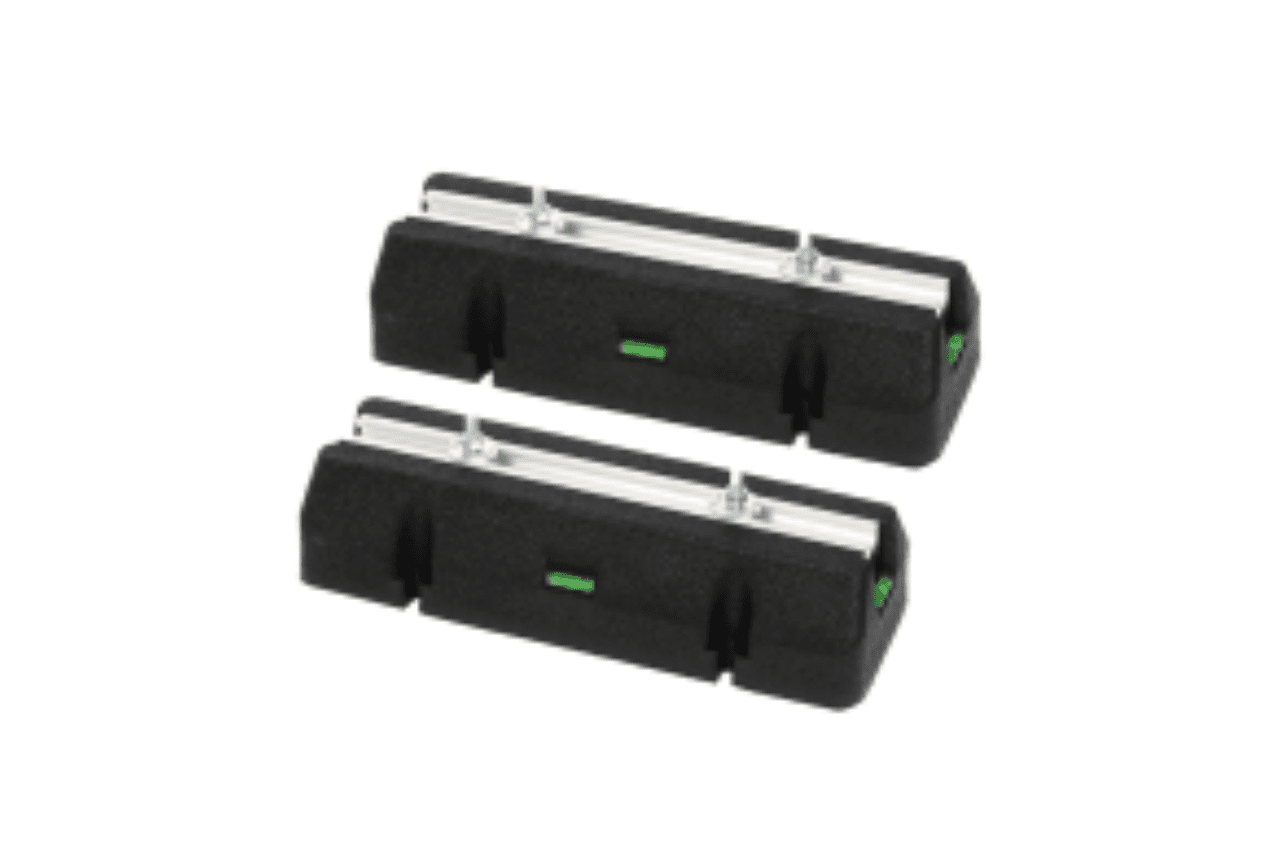
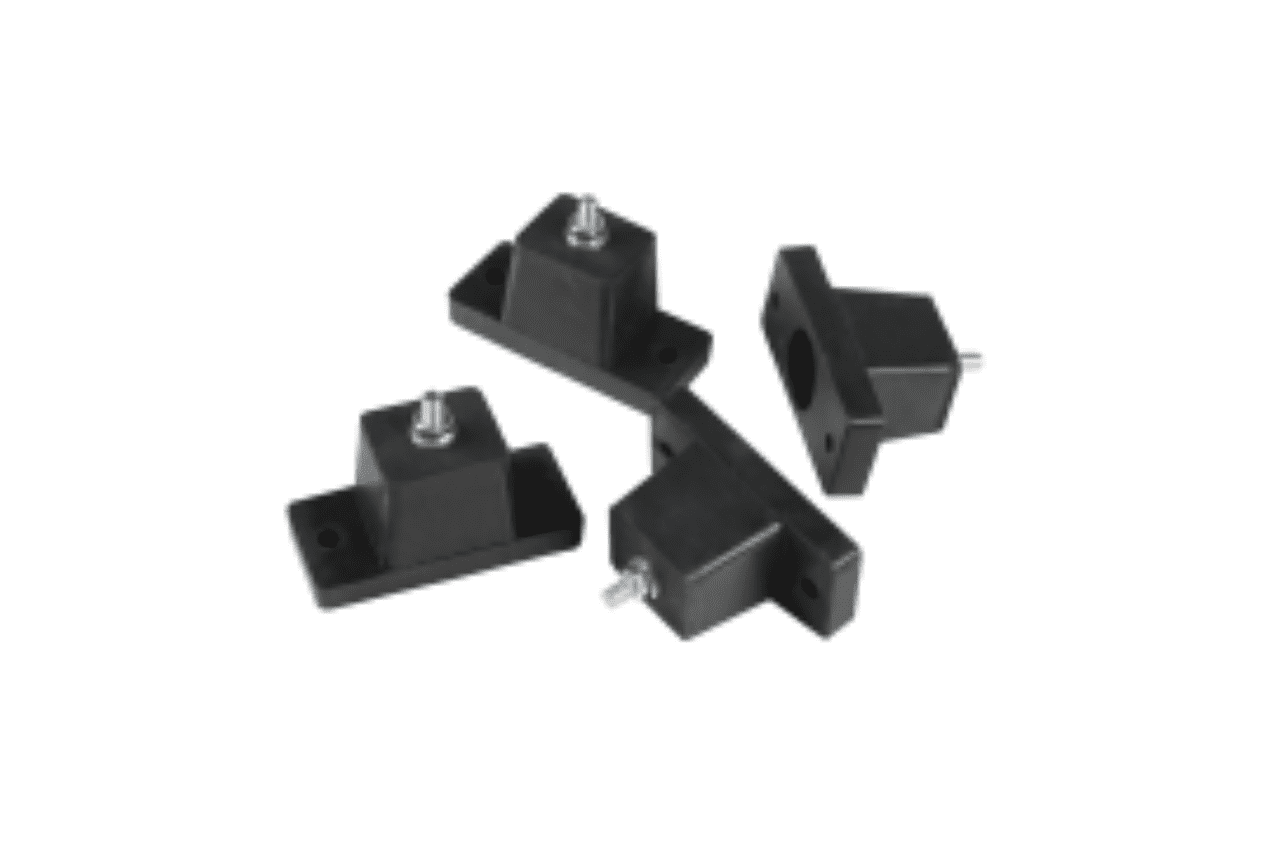
Rubber Vibration lsolator
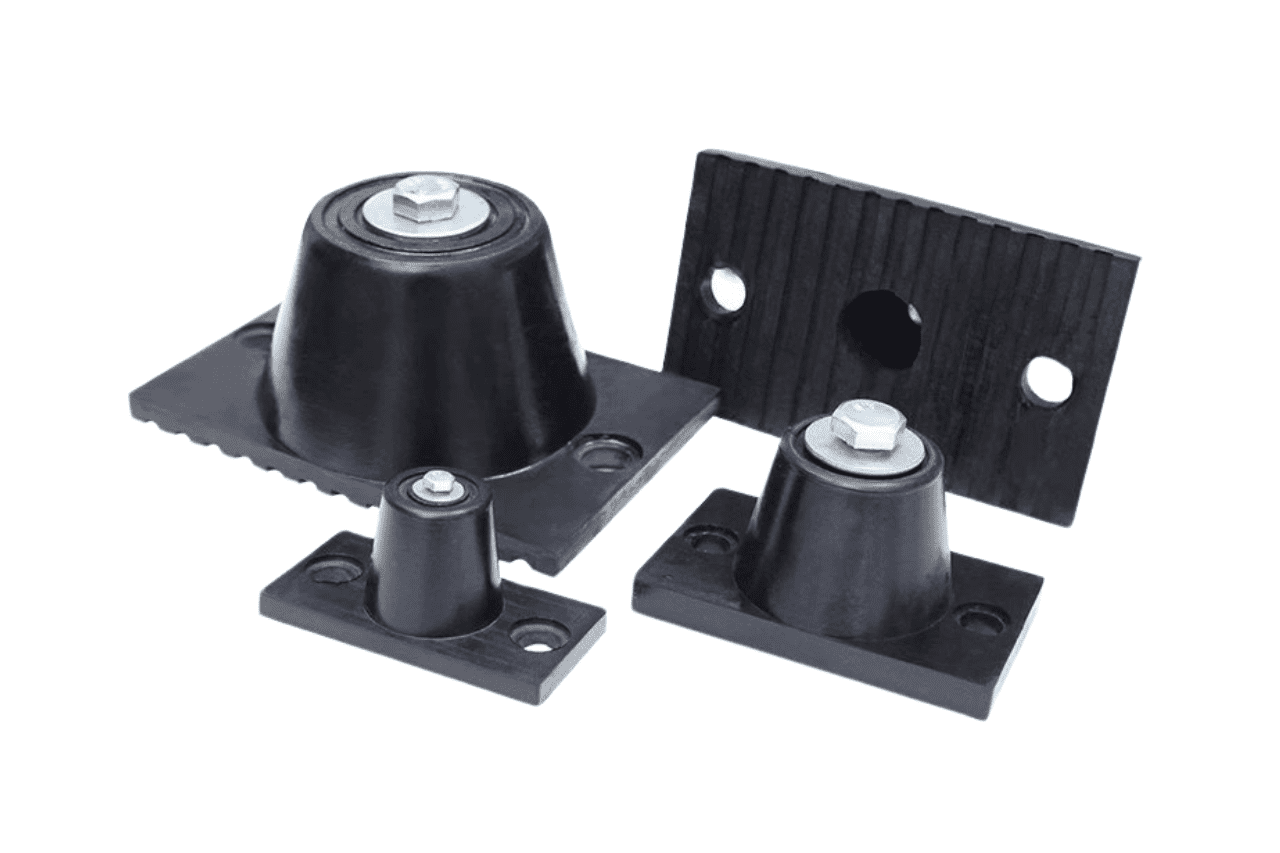

Customizable
Why Choose Us
Trusted Rubber Vibration Isolator Manufacturer with 30 Years of Expertise
Factory-direct solutions with natural rubber, customizable options, reliable quality, and trusted performance.
We own and operate our factory, ensuring strict quality control, stable lead times, and support for small-batch customization
With over three decades in vibration isolation, we offer trusted solutions backed by rich technical knowledge and real-world application.
Our isolators use pure natural rubber for excellent elasticity, durability, and superior shock absorption compared to synthetic materials.
Our ISO-compliant production lines and testing systems ensure consistent quality and reliable performance across all batches.

+86 13032112360
Common Questions
Most Popular Questions
Functions of Rubber Feet
Rubber feet are anti-slip, vibration-dampening pads installed at the bottom of various types of equipment. Their primary role is to prevent devices from sliding or shifting during use, which could lead to operational hazards or damage. Besides providing stability, rubber feet also absorb vibrations generated by machines, significantly reducing noise levels. They act as protective barriers that safeguard both the equipment itself and the surface it rests on. These versatile components are widely used in many industries, including HVAC systems, pump stations, audio equipment like speakers, computers, and various types of industrial machinery.
Anti-Slip Protection
One of the most critical functions of rubber feet is to provide strong frictional grip that prevents equipment from moving unintentionally. This anti-slip feature is especially vital when devices are placed on smooth, glossy, or inclined surfaces where there is a natural tendency for items to slide. By ensuring the equipment stays firmly in place, rubber feet improve safety for operators and prevent potential damage caused by unexpected movements. This function also enhances precision in sensitive devices where even slight shifts can impact performance.
Vibration Isolation
Rubber feet serve as effective vibration isolators by absorbing and dampening mechanical vibrations produced during the operation of equipment. These vibrations, if transmitted directly to floors or mounting structures, can cause noise pollution, premature wear, and structural damage. By isolating the vibrations, rubber feet protect the internal components of machinery, thereby extending their lifespan and maintaining consistent performance. This is particularly important for both small devices such as fans and larger industrial units like air handling systems.
Noise Reduction
Vibrations often translate into unwanted noise, which can create uncomfortable or disruptive environments, especially in residential, commercial, or healthcare settings. Rubber feet help mitigate this issue by acting as sound dampeners. They reduce the transmission of noise from equipment to floors or surrounding structures, thereby improving acoustic comfort. This noise reduction is crucial for maintaining a peaceful and productive environment, and it supports compliance with noise regulation standards in workplaces and public spaces.
Surface Protection
Another significant benefit of rubber feet is their ability to protect floors and surfaces from damage. Heavy or vibrating equipment can cause scratches, dents, or marks on delicate materials such as wood flooring, tile, or glass countertops. The cushioning effect of rubber feet distributes the weight of the device more evenly and reduces the direct pressure exerted on the surface. This protective layer helps maintain the aesthetic and structural integrity of floors and furniture, preventing costly repairs and replacements.
Extending Equipment Lifespan
By minimizing movement, vibration, and shock, rubber feet play an essential role in prolonging the operational life of equipment. Reducing mechanical stress on electronic components and moving parts helps prevent early failure and reduces maintenance needs. This increased durability means fewer breakdowns and less downtime, which is beneficial for both manufacturers and end-users. Over time, the presence of well-designed rubber feet can significantly improve the total cost of ownership for industrial machinery and consumer devices alike.
The Role of Rubber Feet in Vibration Isolation
Rubber feet are commonly used components designed not only to provide stability but also to isolate vibrations from equipment to the supporting surface. By acting as a flexible buffer, rubber feet absorb and dissipate mechanical energy generated by vibrating machinery, preventing it from transferring to floors, walls, or other connected structures.
How Rubber Feet Absorb Vibrations
Rubber material inherently possesses elastic properties and high damping capacity, which means it can deform slightly under pressure and return to its original shape without permanent damage. This elasticity enables rubber feet to absorb the shock and vibrational forces, reducing the amplitude and frequency of vibrations transmitted beyond the equipment base. This mechanism is especially effective for isolating low to medium-frequency vibrations typically found in HVAC units, pumps, and electronic devices.
Comparison with Other Vibration Isolation Methods
While rubber feet provide good vibration isolation for many applications, their performance may be limited compared to specialized solutions such as spring isolators or air mounts. Spring isolators can handle heavier loads and isolate a wider range of frequencies, especially low-frequency vibrations, whereas rubber feet are more suited for lighter equipment and moderate vibration levels. However, rubber feet offer advantages in terms of cost, simplicity, maintenance-free operation, and compact size, making them ideal for many common industrial and commercial uses.
Practical Applications of Rubber Feet for Vibration Control
In everyday applications, rubber feet are widely used under HVAC equipment, pumps, compressors, audio systems, computer hardware, and laboratory instruments. Their vibration isolating function reduces noise, prevents damage to sensitive components, and enhances user comfort and safety. For small to medium machines, rubber feet often provide a highly cost-effective and easy-to-install vibration control solution.
Limitations and Considerations
Despite their benefits, rubber feet have limitations in isolating very high-impact vibrations or heavy industrial machinery with significant dynamic loads. In such cases, a combination of rubber feet with other isolation systems or more advanced vibration isolators may be necessary. It is important to select rubber feet with appropriate hardness (durometer), size, and design to optimize vibration isolation performance for each specific use case.
Conclusion
Rubber feet do indeed help with vibration isolation by absorbing and reducing mechanical vibrations transmitted from equipment to their surroundings. While not always the perfect solution for every scenario, they are an effective, affordable, and widely used choice for vibration control in many industrial and commercial applications.
The Importance of Anti-Slip Properties in Rubber Feet
Rubber feet are widely recognized for their anti-slip capabilities, which is one of their fundamental roles in ensuring equipment stability. When placed under machines or devices, rubber feet provide a reliable grip on various types of surfaces, preventing accidental movement or sliding that could lead to equipment damage or safety hazards.
How Rubber Feet Achieve Anti-Slip Function
The anti-slip effect of rubber feet comes primarily from the natural high coefficient of friction between rubber and most floor materials such as wood, tile, metal, and concrete. This frictional force helps the equipment maintain its position, especially under operational conditions that may induce vibration, shocks, or tilting. The rubber’s flexibility also allows it to conform slightly to uneven surfaces, increasing contact area and grip.
Applications Requiring Strong Anti-Slip Performance
Anti-slip rubber feet are essential in environments where equipment stability is critical — such as in laboratories, manufacturing floors, home appliances, and medical facilities. In places where floors may be smooth, wet, or inclined, rubber feet reduce the risk of slipping, which protects both the machinery and the users.
Comparing Rubber Feet with Other Anti-Slip Solutions
While other anti-slip solutions like adhesive pads, metal clamps, or suction cups exist, rubber feet offer a cost-effective, durable, and maintenance-free alternative. Unlike adhesives, rubber feet can be easily replaced and do not leave residue. Compared to suction cups, rubber feet provide more consistent performance across a variety of surfaces and temperatures.
Design Considerations for Optimal Anti-Slip Performance
The anti-slip efficiency of rubber feet depends on several factors including hardness (durometer), surface texture, and shape. Softer rubber typically provides better grip but may wear faster, while textured or patterned rubber surfaces enhance friction. Choosing the right rubber compound and design ensures the rubber feet can handle specific environmental challenges while providing long-lasting anti-slip protection.
Conclusion
Rubber feet are highly effective in providing anti-slip protection, helping equipment stay securely in place under various conditions. Their combination of frictional grip, flexibility, and durability makes them indispensable components in many industrial, commercial, and residential applications where safety and equipment stability are priorities.
Overview of Core Roles of Rubber Feet
Rubber feet serve as crucial support components for equipment, performing multiple functions such as vibration isolation, anti-slip, and protection for both devices and flooring. Their elasticity and frictional properties significantly enhance equipment stability and safety during operation.
Vibration Damping and Shock Absorption
Rubber feet effectively absorb vibrations and shocks generated during equipment operation, reducing noise and mechanical wear. By cushioning impacts, they help extend equipment lifespan and lower maintenance costs, especially for industrial machinery requiring long-term stable performance.
Anti-Slip and Stability
Thanks to rubber's high coefficient of friction, rubber feet prevent equipment from sliding or shifting, ensuring stable placement in various working environments. This is critical for operational safety and optimal equipment performance, particularly in settings with frequent vibrations or slippery floors.
Protection for Equipment and Floors
Rubber feet protect the bottom of equipment from damage by hard surfaces and prevent scratches or dents on floors caused by direct contact. By cushioning and distributing pressure, rubber feet maintain the integrity of both equipment and flooring.
Insulation and Corrosion Resistance
Certain rubber materials provide excellent electrical insulation, preventing static buildup and electrical hazards. Additionally, their water and chemical resistance help protect equipment from environmental moisture and corrosion.
Conclusion
Rubber feet offer versatile functions including vibration damping, anti-slip, and protective roles. Proper selection and application of rubber feet significantly contribute to equipment stability and longevity, making them indispensable accessories for both industrial and everyday equipment.
In industrial settings, heavy equipment such as compressors, pumps, HVAC systems, CNC machines, and generators generate intense vibrations during operation. If these vibrations are not properly controlled, they can cause structural damage to floors, increase noise levels, and accelerate mechanical wear and tear. The key challenge is finding a solution that can both support heavy loads and provide effective vibration damping.
Rubber feet are an efficient and cost-effective solution designed to withstand high loads. They not only support the weight of heavy equipment but also absorb mechanical energy, reducing noise and vibration in industrial environments.
Yes, rubber feet are suitable for heavy equipment when selected with the appropriate materials, hardness, and structural strength.
Why Rubber Feet Can Support Heavy Machinery
Rubber feet designed for heavy equipment differ significantly from those used on small appliances. They are typically made from high-density natural rubber, neoprene, or other reinforced elastomers, offering excellent compression resistance and load distribution. Some models also include embedded metal components, anti-slip bases, or ribbed structures to enhance stability and support.
These feet serve two main functions:
Load Support: They withstand static and dynamic loads without excessive deformation or compression.
Vibration Isolation: They reduce vibration transmission to floors or mounting surfaces, protecting both the equipment and surrounding structures.
Key Features of Heavy-Duty Rubber Feet
When choosing rubber feet for heavy machinery, the following design aspects are important:
Reinforced Structure: Embedded steel plates or threaded studs improve load capacity and ensure secure installation.
High Hardness Rating: Typically between 60–80 Shore A, providing the right balance of firmness and elasticity under heavy loads.
Chemical and Oil Resistance: Industrial environments often expose components to oils and chemicals; materials like neoprene or EPDM are preferred.
Anti-Slip Design: Ribbed or textured bases prevent movement under high vibration conditions.
Common Applications
Heavy-duty rubber feet are widely used in:
Industrial HVAC systems
Pumps and chillers
CNC machining centers and presses
Diesel generators and compressors
Commercial kitchen equipment
In these applications, rubber feet protect floor structures, extend equipment lifespan, and reduce maintenance requirements.
How to Select the Right Rubber Feet for Heavy Equipment
When selecting rubber feet for heavy machinery, consider:
Load per Foot: Calculate the total equipment weight and distribute it evenly across all support points.
Dynamic vs. Static Load: Account for whether the equipment is stationary or produces movement and impact forces.
Environmental Conditions: Temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals affect material choice.
Consulting with a vibration isolation specialist or manufacturer can ensure the best product is selected for safety and performance.
Conclusion
Rubber feet are more than simple supports—they are engineered components designed to support heavy machinery while minimizing vibration and noise. With proper material selection and design, they offer a cost-effective solution that enhances equipment stability, safety, and longevity. For industrial applications requiring high stability and vibration control, rubber feet are not just suitable—they are essential.
Vibration generated during equipment operation can negatively affect performance, cause structural damage, increase noise, and lead to operator discomfort. Rubber feet, as common vibration isolation components, effectively mitigate and reduce equipment vibration, protecting both machinery and its surroundings.
Sources and Harms of Vibration
Machines like pumps, compressors, and fans generate mechanical vibrations during operation. These vibrations transmit through equipment bases to floors and support structures, causing noise propagation and structural fatigue. Prolonged vibration may affect instrument accuracy and reduce productivity.
Vibration Isolation Principle of Rubber Feet
Rubber feet absorb and dampen vibration energy through their elasticity and damping properties. The rubber material’s high modulus and damping convert mechanical vibration into heat, reducing transmission. Different hardness and thickness levels tailor isolation effectiveness for various vibration frequencies and amplitudes.
Design Factors of Rubber Feet
Effective vibration isolation requires proper design of shape, size, and material. Thicker or corrugated rubber feet provide enhanced cushioning. Some models incorporate metal inserts for improved load capacity and installation stability.
Application Examples
Rubber feet are commonly used on industrial equipment such as Air Handling Units (AHU), Fan Coil Units (FCU), pumps, and compressors to control vibration and noise. They also protect equipment bases and floors, extending service life.
How to Choose the Right Rubber Feet for Vibration Isolation?
When selecting rubber feet, consider equipment vibration frequency, weight, operating environment, and installation conditions. Vibration testing or consulting specialists is recommended to ensure optimal isolation performance.
Rubber pads are versatile, flexible, and highly durable components made from various rubber materials engineered to provide shock absorption, vibration reduction, surface protection, and cushioning in both mechanical and structural applications. Due to their elasticity and resilience, rubber pads play a crucial role in minimizing wear and tear on equipment, reducing operational noise, and extending the lifespan of machinery and infrastructure. These pads come in many forms, including flat sheets, strips, molded shapes, or custom designs, allowing them to be tailored to a wide range of industrial and commercial needs.
Protecting Surfaces from Damage
One of the primary functions of rubber pads is to protect surfaces from damage caused by heavy or vibrating equipment. For instance, when heavy machinery is installed on concrete or metal floors, direct contact can cause cracks, scratches, or dents. Rubber pads serve as an effective buffer layer that distributes weight evenly and cushions impacts, preserving the integrity of the floor and reducing maintenance costs.
Vibration Isolation and Noise Reduction
Rubber pads isolate vibrations produced by motors, compressors, pumps, or HVAC units, preventing the transfer of vibrations to building structures and thus reducing noise pollution and structural fatigue. This isolation not only improves the working environment by lowering noise levels but also protects the building infrastructure from premature wear caused by constant vibrations.
Enhancing Stability with Non-Slip Support
Rubber pads also provide essential non-slip support, ensuring that equipment, furniture, or appliances stay securely in place, even in environments prone to moisture or vibration. This anti-slip feature enhances workplace safety by minimizing accidental movement that could lead to damage or injury.
Sealing and Protective Functions
Beyond cushioning and support, rubber pads often serve as seals or gaskets in assemblies. They help create airtight or watertight joints that protect sensitive components from dust, moisture, and contaminants, ensuring the reliability and longevity of the equipment.
Wide Range of Industrial Applications
Rubber pads have diverse applications across multiple industries. In manufacturing plants, they support heavy machinery, reducing vibrations that could otherwise cause misalignment or premature wear of parts. In the electronics sector, cushioned mounting pads prevent damage during operation or transport. They are commonly used as anti-slip feet on furniture, household appliances, and office equipment, protecting floors and enhancing stability.
Critical Role in Automotive and Construction Sectors
In the automotive industry, rubber pads safeguard fragile parts and reduce noise and vibration, contributing to a smoother and quieter driving experience. Construction projects use rubber pads to protect structural elements and mitigate vibrations from heavy equipment and tools, preserving building integrity and worker safety.
Essential Component in HVAC and Pump Systems
Rubber pads are vital in HVAC systems, pumps, and compressors, acting as mounting pads that stabilize equipment, reduce vibration transmission, and improve operational efficiency. By absorbing shocks and vibrations, they extend the service life of these systems, decrease downtime, and enhance overall performance.
Conclusion
In summary, rubber pads are indispensable components valued for their ability to protect surfaces, absorb vibrations, provide cushioning, and enhance stability and safety. Their adaptability to various shapes, sizes, and materials makes them essential across mechanical, industrial, commercial, and everyday applications. Whether protecting a factory floor or stabilizing household appliances, rubber pads contribute significantly to equipment longevity, noise reduction, and reliable operation.
The weight-bearing capacity of rubber pads depends on their material type, density, thickness, and structural design. Generally, high-quality industrial-grade rubber pads can support loads ranging from hundreds of kilograms to several tons. For instance, solid rubber pads commonly used in machinery installations possess excellent compressive strength, effectively supporting the self-weight and operational loads of heavy equipment.
Material Affects Load Capacity
Different types of rubber—such as natural rubber, nitrile rubber (NBR), and neoprene—exhibit distinct physical properties. For example, nitrile rubber is known for its outstanding oil resistance and low compression set, making it ideal for heavy-duty industrial environments. Neoprene rubber, on the other hand, performs well in outdoor or weather-exposed settings due to its superior resistance to aging and ozone.
The Role of Thickness and Dimensions
The thicker and broader the rubber pad, the better its ability to distribute weight and absorb pressure. Thicker rubber pads provide more cushioning and compressive support, making them suitable for applications involving heavy equipment or concentrated point loads. Selecting the right size ensures stability and long-term performance.
Reinforced Designs for Extra Strength
In certain applications, rubber pads are designed with added reinforcement, such as embedded fibers, ribs, or multilayer composites. These enhancements improve the pad's ability to evenly distribute stress, resist deformation, and maintain durability under high loads.
Common Use Cases
Rubber pads are widely used in HVAC systems, heavy machinery, power generation units, compressors, and pump installations as weight-bearing and vibration-absorbing elements. In environments where both static loads and vibrations coexist, the right rubber pad helps minimize wear, reduce noise, and improve overall system performance.
Conclusion
The load capacity of rubber pads varies greatly depending on the material composition, thickness, and structural design. Choosing the right rubber pad for your equipment not only ensures safe and stable operation but also extends the service life of both the pad and the equipment it supports. Proper evaluation and selection are key to achieving optimal performance in demanding industrial and commercial settings.
Rubber pads are generally waterproof, making them ideal for use in environments where exposure to moisture, water, or other liquids is common. The inherent properties of rubber—especially synthetic types like neoprene, EPDM, and nitrile rubber—offer excellent resistance to water penetration, swelling, and degradation, ensuring long-term performance even under wet or humid conditions.
Waterproof by Nature
Most rubber materials are naturally impermeable to water. This makes rubber pads a preferred choice for applications where water resistance is crucial, such as outdoor equipment bases, marine systems, or environments with frequent washdowns. Unlike porous materials, rubber does not absorb moisture, which prevents structural weakening and microbial growth.
Types of Waterproof Rubber Materials
Among rubber types, neoprene and EPDM are particularly well-suited for waterproof applications. Neoprene offers excellent resistance to water, oils, and UV exposure, making it a top choice for outdoor or marine settings. EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer) rubber excels in resisting water, steam, and harsh weather conditions, and is commonly used in HVAC systems, roofing seals, and automotive weatherstrips.
Applications in Wet Environments
Rubber pads are often used under washing machines, dishwashers, water pumps, or in HVAC systems where condensation and drainage are routine. In construction, waterproof rubber pads serve as buffers and protective layers between structural elements exposed to rain or moisture.
Benefits of Waterproofing
Using waterproof rubber pads prevents corrosion and damage to the equipment and the surfaces they rest on. They reduce the risk of mold, mildew, or bacterial growth in damp settings. This not only extends the pad’s lifespan but also improves overall hygiene and safety in industrial or household environments.
Conclusion
Rubber pads are indeed waterproof and are engineered to perform well in both dry and wet conditions. By selecting the appropriate type of rubber for your specific environment, you can ensure reliable water resistance, mechanical protection, and long-term durability in your equipment support or isolation systems.
Rubber pads play a vital role in both industrial and everyday applications, especially in environments involving elevated temperatures. When made from the appropriate high-performance rubber materials, rubber pads can effectively resist heat, maintain elasticity and structural integrity, and continue to provide reliable shock absorption and insulation under thermal stress.
Heat Resistance Varies by Rubber Type
Different rubber types have different levels of heat resistance:
Silicone Rubber: Known for its superior thermal stability, silicone rubber operates continuously from -50°C to +230°C and can withstand short-term exposure up to 300°C. It is ideal for food processing machinery, medical equipment, and heat-insulating electronics.
EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer): Offers stable performance up to 120°C and excellent resistance to ozone, UV, and weather. Commonly used in automotive seals, roofing membranes, and hot air ducting.
Fluoroelastomer (FKM/Viton®): Endures up to 250°C and is extremely resistant to chemical exposure. It's preferred in aerospace, petrochemical, and advanced mechanical systems.
Nitrile Rubber (NBR): Well-known for oil resistance, but its heat tolerance is relatively lower—typically up to 100°C—suitable for applications with exposure to lubricants and hydraulic fluids.
Common Applications in High-Temperature Settings
Rubber pads are extensively used in high-temperature environments such as:
Machinery mounting bases: For dryers, heaters, and compressors, providing insulation, shock absorption, and vibration damping;
High-temp gaskets and seals: Used in boilers, exhausts, and heat exchanger joints to prevent heat and gas leakage;
Electronics cushioning pads: To prevent damage or circuit failure due to thermal expansion and vibrations;
Automotive and rail applications: Near engines, exhaust systems, and brake systems to isolate heat and vibration.
Key Advantages of High-Temperature Rubber Pads
Preserve structural integrity: Resistant to melting or deformation under continuous heat exposure;
Extend equipment life: Protects machinery from heat-induced wear and fatigue;
Insulation performance: Rubber’s low thermal conductivity creates an effective heat barrier;
Versatile durability: High-temp rubber is also resistant to ozone, moisture, and aging, suitable for harsh conditions.
Proper Material Selection is Critical
Not all rubber pads are designed for high-heat applications. Choosing the right material depends on the maximum working temperature, duration of exposure, and environmental factors such as steam, oil, or chemicals. Professional manufacturers often provide customized solutions, including reinforced rubber pads or multilayer composites, to meet specific operational requirements.
Conclusion
Rubber pads can indeed withstand high temperatures—but only if the correct heat-resistant rubber material is used. Options like silicone, EPDM, and fluoroelastomers offer excellent thermal resilience and are suited to demanding thermal environments. By selecting the right material and design, rubber pads can deliver exceptional performance, ensuring safety, durability, and stability for your equipment.
Rubber pads are highly effective in preventing slipping, which is why they are widely used under equipment, furniture, and in various industrial applications. Their high coefficient of friction allows them to grip surfaces firmly, helping to prevent movement caused by vibration, pushing, or uneven floors.
What Makes Rubber Pads Slip-Resistant?
The slip-resistance of rubber pads comes from their natural elasticity and high frictional grip. Even on smooth or inclined surfaces, rubber pads conform to the floor and distribute pressure evenly, providing solid support. Many pads are also designed with anti-slip textures like grooves, granules, or honeycomb patterns to further increase traction and floor adherence.
Applications in Slip Prevention
Furniture and Appliances: Placing rubber pads under refrigerators, washing machines, sofas, or desks prevents floor scratches and unwanted movement.
Industrial Equipment: Heavy machinery such as compressors and pumps can shift due to vibration; rubber pads help prevent sliding while damping shocks.
Stairs and Ramps: Anti-slip rubber strips or pads are commonly used in public areas like malls, hospitals, or metro stations to improve traction on steps or inclined surfaces.
Automotive Use: Rubber mats or pedal pads add grip, enhancing driving safety and preventing foot slips.
Matching Pads to Surfaces and Loads
Although rubber pads generally offer good slip resistance, effectiveness depends on factors like surface type (tiles, wood, concrete), load weight, and pad thickness. In oily or wet conditions, special oil-resistant or textured rubber pads should be used to maintain performance.
How to Enhance Slip-Resistance?
Choose pads with embossed or patterned anti-slip surfaces;
Look for products labeled “high-friction” or “non-slip”;
Clean the bottom of the pads and the floor regularly to prevent slippage;
For heavy equipment, consider thicker or bolted rubber pads for better stability.
Conclusion
Rubber pads are excellent for preventing slips and movement in a variety of settings, from furniture and machinery to stairs and vehicles. With proper selection and maintenance, they provide safety, surface protection, and increased stability.
Yes, rubber pads can be used outdoors, provided that the right materials and designs are selected to withstand environmental exposure. Outdoor conditions bring unique challenges such as UV radiation, rain, temperature fluctuations, oil, and dust. Quality rubber pads are engineered to endure these elements while maintaining performance and durability.
Best Rubber Materials for Outdoor Use
EPDM Rubber: Ideal for outdoor applications due to its superior resistance to UV rays, ozone, and weathering. It remains stable under sunlight and moisture for long periods.
Neoprene Rubber: Known for its resistance to heat, oil, and chemicals. It performs well in marine or industrial outdoor environments.
Natural Rubber: While naturally elastic and impact-absorbing, it lacks weather resistance. It should only be used outdoors if treated with protective coatings or used in shaded areas.
Common Outdoor Applications
Support for External Equipment: Such as outdoor HVAC units, pumps, or compressors, where rubber pads help dampen vibration and noise.
Anti-Slip Safety Pads: Installed on outdoor stairs, ramps, or platforms to prevent slips and falls in wet or sloped areas.
Playgrounds and Fitness Zones: Rubber mats are used for cushioning impact in parks, schools, and public gyms to reduce injury risk.
Vehicles and Infrastructure: Durable pads are used in parking lots, toll booths, or beneath traffic systems for vibration isolation.
Tips for Outdoor Use and Maintenance
Choose pads labeled “weather-resistant” or “outdoor grade”;
Inspect regularly for signs of cracking or aging and replace when needed;
Avoid sharp objects or heavy point loads that may damage the pad;
In extreme environments (e.g., tropical heat, icy winters), consider reinforced or thicker versions.
Conclusion
Rubber pads are fully suitable for outdoor applications when made from proper weather-resistant materials. With the right choice and care, they provide long-term benefits including vibration isolation, anti-slip safety, impact cushioning, and surface protection—making them a versatile solution for outdoor environments.





